
Research
The IE department has four laboratories: Human Factors Engineering Lab (HFEL), Logistics Engineering Lab (LEL), Production Engineering Lab (PEL), and Computing and Simulation Lab (CSL).
1 Human Factors Engineering Lab (HFEL)
HFEL serves both for teaching and research. Table 1 lists the objectives, facilities, and supported courses of these sub-Labs.
Table 1 Human Factors Engineering Lab
Physical Ergonomics and Occupational Safety (Room 524A) Objectives: To support teaching and research in anthropometry, physical environment measurement, biomechanics, work analysis, and hazard handling etc. |
|
Facilities |
|
Courses |
|
Management and Organizational Ergonomics (Room 524A) Objectives: To support teaching and research in working team study (individual characteristics, working environment, performance measurement and improvement, etc.) |
|
Facilities |
May use the devices above
|
Courses |
|
Cognitive Ergonomics and Human-Computer Interaction (Room 524B) Objectives: To support teaching and research in developing methods and tools for evaluating and improving human’s performance for information products and services, especially in the cognitive ergonomics and HCI domains. |
|
Facilities |
Usability testing and user study room
|
Courses |
|
Cross-Culture and Ubiquitous Design (Room 524C) Objectives: To support teaching and research in developing methods and tools for studying culture effect for some important aspects, such as hazard perception, interface design, buying decision-making, and internet use interactions. |
|
Facilities |
Usability Lab |
Courses |
|
Usability and User Experience (Room 524D) Objectives: To support teaching and research in developing methods and tools for evaluating and improving the usability and user experience of products and services. |
|
Facilities |
Usability Lab |
Courses |
|
Driving Safety and Human-System Simulation (Room 521B) Objectives: To support teaching and research in developing methods and simulation tools to measure driver’s characteristics, capabilities, and driving skills, and change driver’s intentions for some unsafe behaviors. |
|
Facilities |
Motion tracking system with 8 CCD cameras and human-in-the-loop simulations
|
Courses |
|
Human Error and System Safety (Room 524E) Objectives: To support teaching and research in developing methods and tools for evaluating and analyzing human’s reliability and improving system safety. |
|
Facilities |
Software to simulate nuclear operations.
|
Courses |
|
Social Computing and Mobile Computing (Room 524F) Objectives: To support teaching and research in developing methods and tools for studying social computing and mobile computing. |
|
Facilities |
Usability Lab |
Courses |
|
2 Logistics Engineering Lab (LEL)
LEL was established to support teaching and research. Currently, the experiments for both undergraduate and graduate courses can be conducted in the lab, as shown in Table 2.
Table 2 IE courses served by the LEL
Undergraduate courses |
Graduate courses |
Introduction to Logistics Production Planning and Control Inventory Management Logistics Networks Planning |
Production Management Advanced Inventory Control Advanced Logistics Networks Research Activities |
Figure 1 shows the relationships between logistics system components and four courses, as well as seven related experiments that support the courses. Figure 2 shows the framework and layout of the LEL with four mixed parts. They are mixed model assembly line (MMAL), automatic storage and retrieval system (AS/RS), sorting center, and network platform. Figure 3 shows experimental designs.
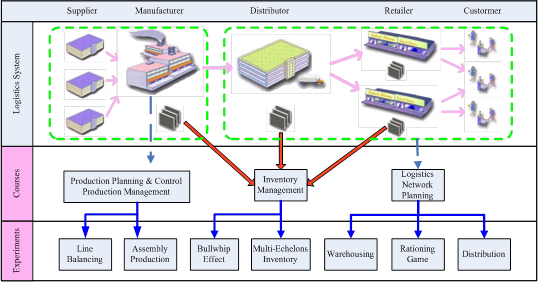
Figure 1 The framework of logistics systems
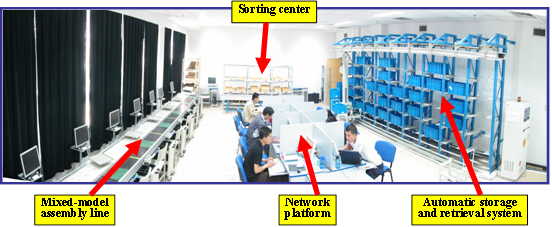
Figure 2 Layout of the Logistics Engineering Lab
Product structure analysis |
Working on the mixed-model assembly line |
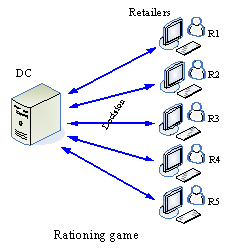
Bullwhip effect |
Structure of the bullwhip effect experiment |
 |
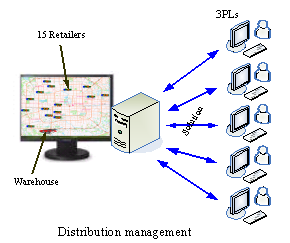 |
Figure 3 Examples of experimental design
Through years of effort, we have achieved significant impact on IE education in China as well as in the world, as proved by the following facts:
The LEL has been the best among the IE programs in China, as unanimously acknowledged by all the attendees.
The LEL has provided laboratory design and construction consultancy for many universities in other IE programs.
The LEL won the 2007 Innovations in Curriculum Award, IIE.
The impact of the LSL extends beyond campus. The industry practitioners in our continuing education programs benefit as well. Through the experiments, they learned to combine their experience with the theories covered in our IE training program.
3 Production Engineering Lab (PEL)
The PEL provides an industry-oriented training platform, prepares students with systematic view and practical skills, and cultivates highly competent industrial engineers for global manufacturing. The objectives of PEL are to become an educational platform for creative thinking in manufacturing engineering and to explore the next generation manufacturing modes.
The PEL is designed to demonstrate a wide collection of industrial systems and provide a platform for research of various manufacturing industries. The following list is the facilities in the lab:
Production lines, including sewing production and assembly lines
Single piece and small batch production with robot operations, CNC milling, and CNC turning
Batch processes with molding production
Continuous processes with bottling
Engraving machine (quantity: 2)
CNC Lathe (1)
Industrial robot (2)
Multi-functional sewing machine (3)
Integrated embroidery and sewing machine (1)
Belt conveyor (1)
Bottling machine (1)
3-D laser scanner (1)
 |
 |
 |
 |
Figure 4 Facilities in the production engineering laboratory
 |
 |
|
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
Figure 5 The Students in the Lab and Products of the Student Experiments
Table 3 lists some of the experiments in courses.
Table 3 IE courses served by the PEL
Experiment |
Course |
CNC programming and machining |
Introduction to Modern Manufacturing System and Experiment (40160573) |
Robot application and simulation |
Manufacturing Systems and Automation (40160183) |
Design and operational management of sewing production systems |
Production Planning and Control (40160173) |
Practice of reverse engineering |
Manufacturing Systems and Automation (40160183) |
Practice of forming production systems |
Fundamentals of Manufacturing Engineering (30160133) |
Design and implementation of chemical processes |
Fundamentals of Manufacturing Engineering (30160133) |
Quality control and management |
Statistical Quality Control (40160203) |
Design and application of production information systems |
Management Information Systems I (40160243) |
4 Computing and Simulation Lab (CSL)
CSL is aimed at providing computing and simulation support for teaching and research for the dep
artment. It was re-constructed in April, 2008, with significant upgrade of high performance computing workstations and software packages. CSL now has two major units, with the high performance computing server groups and workstations located in Room 601, and the system simulation unit located in Room 512. The total space is 120 m2. Currently, CSL has the following hardware facilities:
High performance computing servers such as Sun Fire X4600, HP ProLiant DL580 G5, IBM System X3400, and DELL PowerEdge2900 with high storage capacity devices.
High performance graphic workstation, Sun Ultra 40 with high-end graphics card and high-resolution rendering performance
Thirty-eight high performance computers, each with many software packages installed, for various simulation purposes.
Image acquisition device, projectors, and video- conference system
CSL has the following licensed commercial and self-developed software packages:
Logistics Practice Network Experimental Platform
Production Management System
Modeling software: Matlab, Mathematica,
Statistics and optimization software: MiniTab, Spss, CPLEX, Xpress-MP, etc.
Simulation software: Arena, Enterprise Dynamic, Anylogic, Simo, Flexsim.
Reliability software: Weibull++, ALTA Pro, BlockSim FTI, Xfmea, Lambda Predict
Enterprise Planning Resource software: Proplanner Product Engineer (Time Estimation, Line Balancing, Work Instructions, Ergonomics Assessments)
CAD software: Catia, Pro/Engineer, AutoCAD, 3ds max
Figure 6 shows the logistics system experiment platform software that was developed by ourselves.
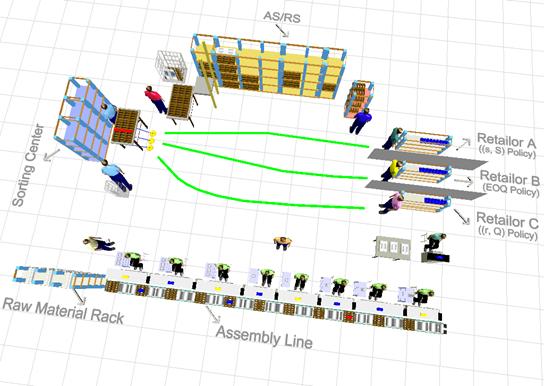
Figure 6 Logistics system experiment platform
CSL supports experiments of the following courses:
Modeling and Simulation (40160083)
Management Information Systems I (40160243)
Introduction to Supply Chain Management (80168122)
Facilities Planning (40160052)
Theory and Practice of Project Management (80160082)
Transportation and Distribution Management (80160322)
Enterprise Information Management (80160032)
Introduction to Modern Manufacturing System and Experiment (40160573)
Distribution Systems Modeling and Analysis (80160152)